In an increasingly connected world, where businesses, individuals, and governments rely heavily on the internet for daily operations, the threat of cyberattacks looms large. Among the most disruptive and damaging of these cyberattacks is the Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. A DDoS attack can cripple a website, disrupt online services, and cause significant financial and reputational damage. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to mitigate the risk of falling victim to such an attack. This article outlines easy, actionable steps you can take to protect yourself or your business from DDoS attacks.
Table of Contents
Understanding DDoS Attacks
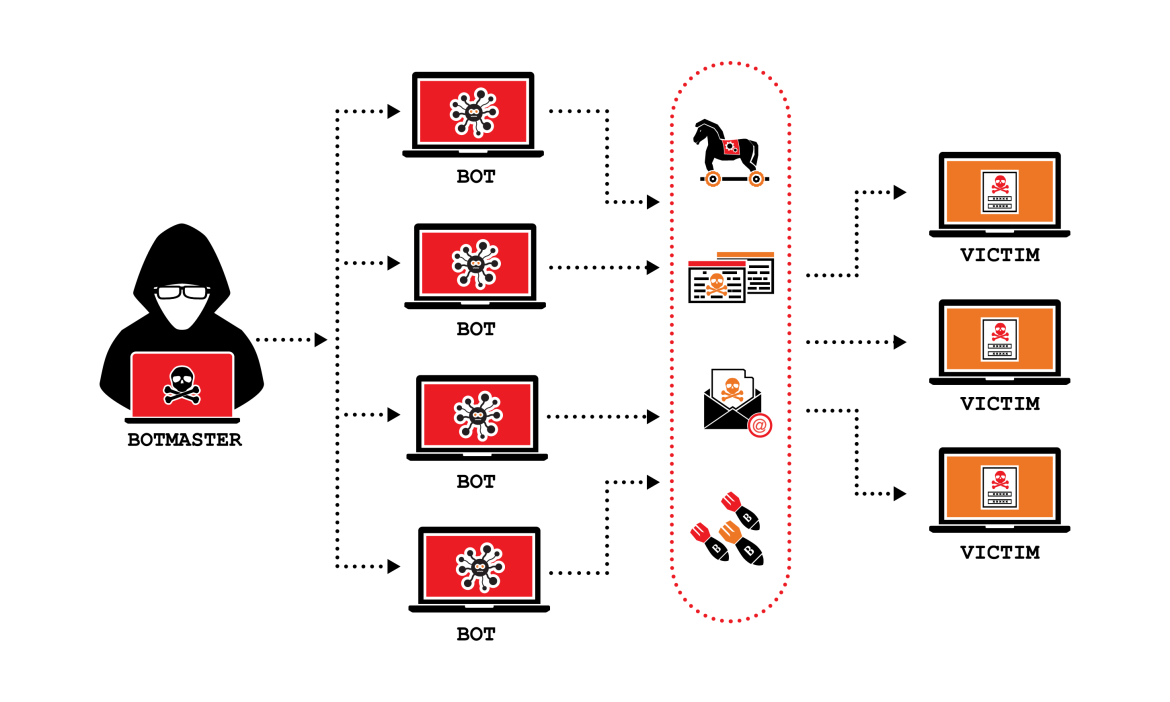
Before diving into the prevention strategies, it’s essential to understand what a DDoS attack is and how it works. A DDoS attack occurs when multiple systems flood the bandwidth or resources of a targeted server, website, or network with an overwhelming amount of traffic. The sheer volume of this traffic can cause the target to slow down or become entirely inaccessible.
Attackers typically use a botnet—a network of compromised computers or other devices—to generate the flood of traffic. The botnet may consist of thousands or even millions of devices, all working together to overwhelm the target. The result is that legitimate users are unable to access the services, leading to disruptions that can last hours, days, or even longer.
Step 1: Understand Your Vulnerabilities
The first step in protecting against a DDoS attack is to understand where your vulnerabilities lie. Conduct a thorough assessment of your online presence, identifying critical assets that could be targeted. These might include:
- Websites: The most common target for DDoS attacks.
- Servers: Critical servers that host essential services or data.
- APIs: Application Programming Interfaces that provide connectivity between different services.
- Cloud Services: Cloud-based resources and applications that are integral to your operations.
By knowing where your vulnerabilities are, you can prioritize your defenses and focus on the areas that are most at risk.
Step 2: Invest in Robust DDoS Protection Services
One of the most effective ways to prevent DDoS attacks is to invest in a robust DDoS protection service. These services are offered by specialized providers and can automatically detect and mitigate DDoS attacks before they reach your infrastructure.
Some well-known DDoS protection services include:
- Cloudflare: Provides comprehensive DDoS protection for websites and applications.
- Akamai: Offers advanced DDoS mitigation with a global network of servers.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Shield: Integrated with AWS to protect cloud-based resources.
- Microsoft Azure DDoS Protection: Tailored for applications hosted on the Azure cloud.
These services work by analyzing incoming traffic in real time and filtering out malicious traffic while allowing legitimate users to access your services. They also scale automatically to handle large-scale attacks, providing an additional layer of security.
Step 3: Implement a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is another critical tool in the fight against DDoS attacks. A WAF is designed to protect your web applications by monitoring and filtering incoming traffic. It can detect and block malicious requests before they reach your application servers.
Some benefits of implementing a WAF include:
- Traffic Filtering: Blocks harmful traffic, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and DDoS attacks.
- Custom Rules: Allows you to create custom rules tailored to your specific application and threat landscape.
- Real-time Monitoring: Provides insights into traffic patterns and potential threats.
By deploying a WAF, you add an extra layer of protection that can significantly reduce the risk of a successful DDoS attack.
Step 4: Use Content Delivery Networks (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of servers distributed across multiple locations. CDNs are designed to deliver content to users more efficiently by caching content closer to the user’s location. In addition to improving website performance, CDNs can also help protect against DDoS attacks.
Here’s how a CDN can protect you:
- Load Distribution: CDNs distribute traffic across multiple servers, making it harder for attackers to overwhelm a single server.
- Geographical Redundancy: By spreading traffic across different regions, CDNs reduce the risk of a localized attack taking down your entire service.
- Traffic Absorption: CDNs can absorb large amounts of traffic, helping to mitigate the impact of DDoS attacks.
Popular CDN providers include Cloudflare, Akamai, and Amazon CloudFront, all of which offer integrated DDoS protection features.
Step 5: Maintain Redundant Infrastructure
Another effective strategy to prevent DDoS attacks is to maintain redundant infrastructure. By spreading your resources across multiple data centers or cloud providers, you reduce the risk of a single point of failure.
Here’s how redundancy can help:
- Load Balancing: Distributes traffic evenly across multiple servers, preventing any single server from being overwhelmed.
- Failover Systems: Automatically switches traffic to backup servers in case of an attack, ensuring continuity of service.
- Geographic Dispersion: Spreads resources across different locations, making it difficult for attackers to target your entire infrastructure.
By maintaining redundant infrastructure, you can ensure that your services remain available even in the face of a DDoS attack.
Step 6: Implement Rate Limiting and Throttling
Rate limiting and throttling are techniques used to control the flow of traffic to your website or application. By limiting the number of requests a single IP address can make in a given period, you can reduce the effectiveness of a DDoS attack.
Key benefits of rate limiting include:
- Prevention of Abuse: Stops malicious users from overwhelming your servers with excessive requests.
- Improved Performance: Ensures that legitimate users can access your services without delay.
- Customization: Allows you to set different rate limits for different types of traffic, providing flexibility in your defense strategy.
Most web servers and WAFs support rate limiting and throttling features, making it easy to implement these defenses.
Step 7: Monitor Traffic Patterns and Anomalies
Continuous monitoring of your traffic patterns is crucial for early detection of DDoS attacks. By establishing a baseline of normal traffic behavior, you can quickly identify anomalies that may indicate an attack.
Some key metrics to monitor include:
- Traffic Volume: Sudden spikes in traffic may signal a DDoS attack.
- Source of Traffic: A high concentration of traffic from a specific region or IP range may indicate malicious activity.
- Response Times: Slower-than-usual response times may be a sign that your servers are under strain from an attack.
By monitoring these metrics in real time, you can quickly respond to potential threats before they cause significant damage.
Step 8: Create an Incident Response Plan
Even with the best defenses in place, it’s important to have an incident response plan ready in case of a DDoS attack. An effective response plan should include:
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly defined roles for each member of your team during an attack.
- Communication Plan: Procedures for informing stakeholders, customers, and the public about the attack.
- Mitigation Steps: A step-by-step guide for mitigating the impact of the attack and restoring services.
- Post-Attack Analysis: A process for analyzing the attack and implementing improvements to your defenses.
By having a well-prepared incident response plan, you can minimize the impact of a DDoS attack and recover more quickly.
Step 9: Educate Your Team
Cybersecurity is a team effort, and educating your staff about the risks and prevention strategies is essential. Regular training sessions can help your team stay informed about the latest threats and best practices for preventing DDoS attacks.
Some key topics to cover in training include:
- Recognizing DDoS Attacks: How to identify the signs of a DDoS attack and respond appropriately.
- Using Security Tools: Training on the use of WAFs, CDNs, and other security tools.
- Incident Response Procedures: Familiarizing the team with the incident response plan and their roles during an attack.
By fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, you can strengthen your defenses against DDoS attacks.
Conclusion
Preventing a DDoS attack may seem daunting, but by taking these easy steps, you can significantly reduce your risk. Understanding your vulnerabilities, investing in robust protection services, implementing a WAF, using CDNs, maintaining redundant infrastructure, and educating your team are all critical components of a comprehensive DDoS prevention strategy. By staying vigilant and prepared, you can protect your digital assets and ensure the continuity of your services in the face of an ever-evolving threat landscape.


